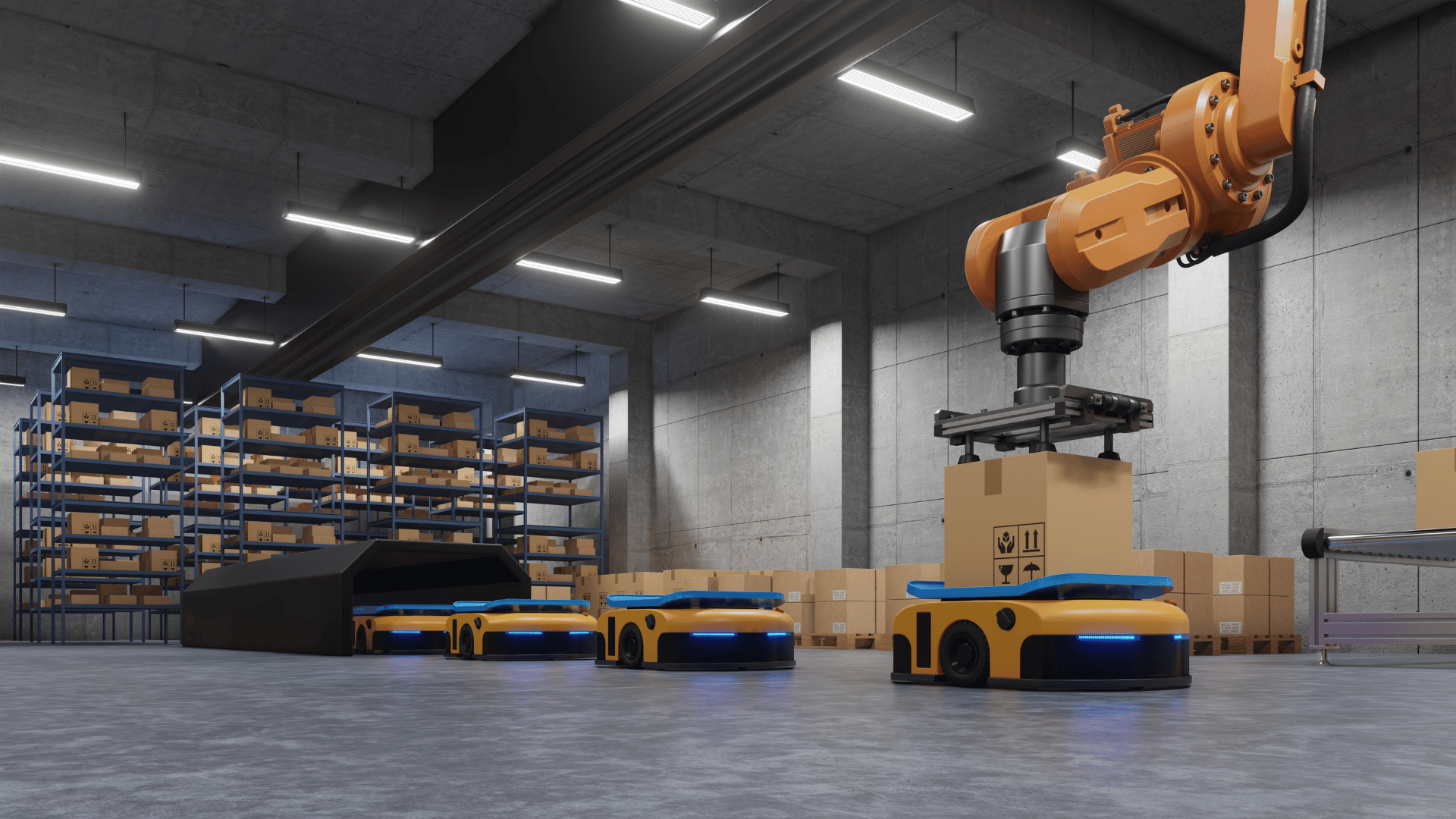
After exploring in part one of our series on the potential of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to revolutionize the logistics industry, now it’s time to focus on the actual implementation of these advanced technologies. Implementing AMRs is not just about acquiring technology; it’s about intelligently and strategically integrating it into a company’s existing structure to increase efficiency and optimise intralogistics workflows.
DAAC digital aims to provide custom solutions that meet each client’s specific objectives, ensuring that the implementation process is smooth and aligned with the highest industry standards. We are committed to turning intralogistics challenges into automation opportunities, using AMRs to open new horizons in operational efficiency and competitive performance.
Now, let’s go through the crucial steps of the implementation process, from planning and setup, to actual deployment and ongoing optimization, all under the expert guidance of DAAC digital.
Stages of Implementation:
1. Implementation Planning:
- Infrastructure analysis: Measuring and mapping storage space to identify optimal routes and staging locations.
- Assessing expectations: Align expectations with technological reality to avoid common pitfalls, such as underestimating the complexity of integration.
- Detailed planning: Establish objectives, identify necessary resources and create a well-defined implementation plan.
2. Technical Setup:
- Network Configuration: Ensure a robust wireless network infrastructure for reliable AMR communication.
- Integration with WMS: Connecting AMRs to warehouse management systems to synchronize operations.
- Sensor calibration: Sensor calibration to recognize obstacles and navigate efficiently.
- Safety testing: Checking safety mechanisms to protect equipment and personnel.
- Rapid Response Team Training: Preparing the team to respond to errors.
- Simulations and operational testing: Run simulations to verify the performance of AMRs in different scenarios.
3. Testing and Evaluation:
- Initial testing: Assess the ability of AMRs to perform basic tasks in a controlled environment.
- Test extension: Testing in real working scenarios, including peak activity.
- Simulating varying conditions: Testing the adaptability of AMRs to changes in warehouse layout.
- Performance analysis: Monitor the efficiency of routes, cycle time and accuracy of tasks.
- Collect feedback: Identify operational difficulties or additional training needs.
- Identifying areas for improvement: Analyze the data to identify patterns of behavior that require optimization.
4. Staff Training:
- Training programs: Introduction to AMR technology, AMR operation and supervision, AMR integration into workflows and safety.
- DAAC digital certifications: consolidating skills acquired in training programmes;
5. Phase-by-phase unfolding:
- Pilot: Start with a pilot in a limited area to test performance and integration.
- Evaluation and adjustment: Analysis of pilot results and adjustment of implementation and configuration strategies.
- Expanding the implementation: Gradually extend the implementation to other areas of operations.
- Continuous optimization: Continuously monitor and adapt AMR usage to meet business needs.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment:
- Performance Monitoring: Understand how AMRs contribute to operational objectives.
- Troubleshooting: Identify and quickly fix technical or operational problems.
- Adapting to change: Adapting to changing demand and optimizing workflows.
The adoption of AMRs is essential to modernise intralogistics processes. DAAC digital provides the support needed to successfully navigate the transition to automation, from technology selection to operational optimization.
The journey to automating logistics with autonomous mobile robots (AMR) doesn’t end here!
See the rest: